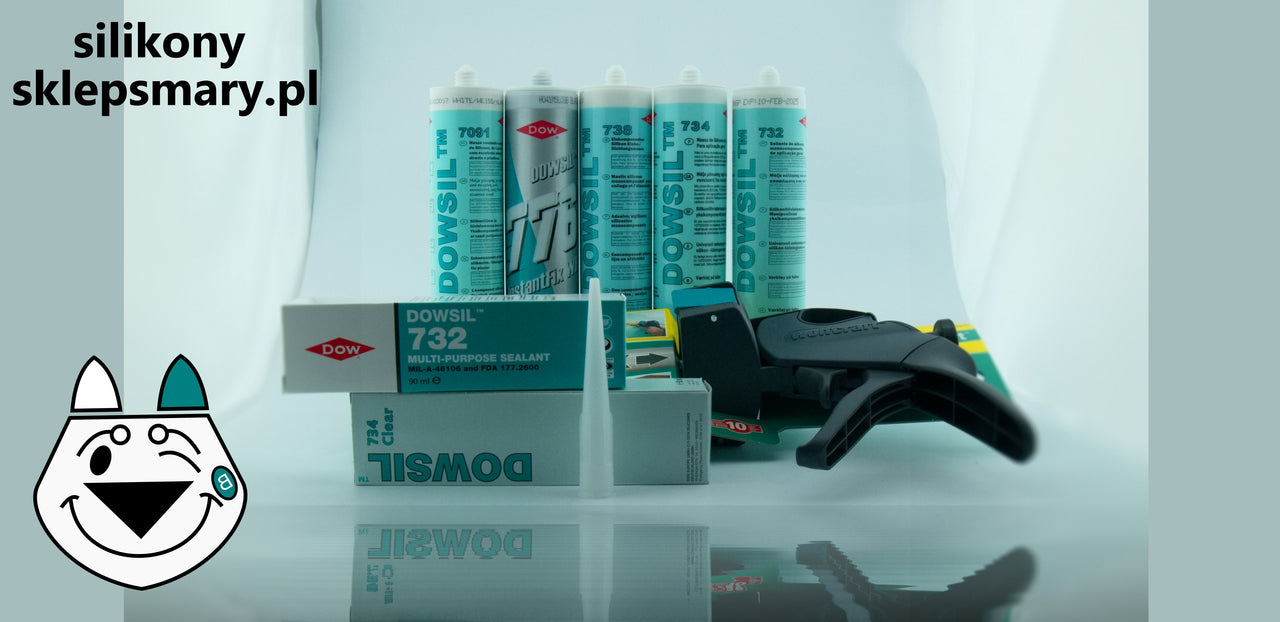
Here are some of the main features of silicone glue:

Flexibility : Silicone adhesive is very flexible, meaning it can withstand movement and deformation of the surfaces it bonds. This is especially useful for materials with different thermal expansions, such as metal and glass.

Waterproof : Silicone adhesives are waterproof, meaning they can be used in humid environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoors. Silicone does not lose its adhesive properties even in the presence of water.

Chemical resistance : Silicone is also resistant to many chemicals, such as oils, fats, acids and alkalis. Therefore, silicone adhesive can be used in various industries, including automotive and chemical.

Resistance to high and low temperatures : Silicone is stable over a wide range of temperatures, from very low to very high. Silicone adhesives can therefore be used in extreme conditions, such as car engines or electronic devices.

Electrical insulation called dielectricity : Silicone glue has insulating properties, which means it can be used to connect electronic components. It protects against the flow of current and protects connections from moisture and other external factors.

Wide range of applications : Silicone adhesives are used in various fields such as construction, automotive, electronics, home improvement and many others. They can bond various materials such as metal, glass, ceramics, wood, plastics and many others.

It is important to remember that silicone adhesives also have some limitations. An overview of the most important difficulties associated with the use of silicone includes the following limitations:

Temperature : Silicone is relatively thermally stable, but it does have its limitations. At high temperatures (above 200-250°C), silicone can degrade, leading to reduced strength and flexibility.

Chemicals : Silicone is resistant to many common chemicals, such as water, detergents, and some acids. However, it can decompose in the presence of some strong bases, organic solvents, and some chemicals.

UV exposure : Silicone is sensitive to UV radiation, which can cause it to degrade. Therefore, silicone is not recommended for outdoor use without additional protection, such as protective coatings or UV dyes.

Adhesion : Silicone has poor adhesion to some materials, such as some plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene.

Mechanical strength : Silicone is a flexible material, but has limited mechanical strength compared to some other materials such as steel or aluminum, epoxy adhesives.

Abrasion Resistance : Silicone is susceptible to abrasion and scratching. For applications where there is intense friction or exposure to mechanical damage, additional protection such as a protective coating or other more abrasion-resistant materials should be considered.

Curing time : Silicone is a material that cures by reaction with atmospheric moisture and such access to moisture must be maintained throughout the curing process.

Required Surfaces : Silicone may require properly prepared surfaces to bond and cure effectively. Improper surface preparation, such as the presence of oils, grease or other contaminants, can result in poor adhesion and inadequate cure of the silicone.

Biocompatibility : Silicone is often used in medical applications, but it is important to ensure that the silicone in question is properly tested and meets biocompatibility requirements.

Costs : Silicone can be a relatively expensive material compared to some other options. Budget constraints may influence the choice of silicone as a material in some applications.
It is important to carefully consider the above limitations and tailor the use of silicone to the specific conditions and requirements of the application.