Sort + Filter
What is Grease? - Choosing a Grease
Greases are lubricants that provide specific performance properties where lower viscosity oils simply do not perform.
Greases consist of three basic types of ingredients, a high quality base oil, a thickener system and various performance enhancing additives.
These versatile lubricants have slightly different compositions, but each grease has a similar ingredient breakdown: 80% to 90% base oil, 10% to 20% thickener, and 3% to 5% additive.
Greases are ideal solutions for industrial applications where low viscosity fluids do not provide adequate protection or in-situ durability.
Simply put, grease essentially acts like a sponge, with a thickener system holding the lubricating oil in place and releasing fluid under pressure to prevent wear and damage to the metal surface.
Base oils
Base oil is the liquid component of each grease is a typical lubricating oil – it can be mineral oil, silicone, synthetic or any liquid with lubricating properties. and a level of viscosity level.
Thickeners
The main thickeners used in the production of greases are lithium, aluminum, calcium, bentonite and polyurea, available individually or in various configurations.
Lubricant additives
Additives impart or modify the properties of lubricants. These are mainly: corrosion and oxidation inhibitors, depressants regulating the flow temperature, solid lubricants or friction reducing agents: molybdenum disulfide, graphite and dyes.
What are lubricants used for:
- They prevent surface wear
- They reduce metal friction - anti-seize pastes
- They work as a sealant - silicone sealing compounds
- Protect against rust and corrosion - coatings
- Reduce noise and vibration

How to choose the right lubricant?
There are many different industrial greases, semi-fluid, lithium-containing, synthetic or mineral oil based.
For the average person, choosing a lubricant can be confusing - where to start?
There are four main factors that help narrow down the selection of suitable lubricants:
- Load
- Environment
- Temperature
- Speed
| Load | The amount of force/stress exerted on a component or surface. (Light, medium, or heavy) |
| Environment | Work environment, including low and high temperatures, humidity, exposure to water, chemicals or fuels, and other airborne contaminants |
| Temperature | Operating temperature of the device or surface, including ambient temperature and peak low and high temperatures |
| Speed | The type of movement, revolutions per minute, can be classified as low to high speed. |
Common grease lubrication difficulties
As any lubrication engineer knows, there are many obstacles that greases or other fluids must overcome during normal operation. The following are the most common difficulties that lubricants face.
- Warm
- Pollution
- Miscibility of greases
- Over-lubrication
- Incorrect lubricant
Grease NLGI consistency
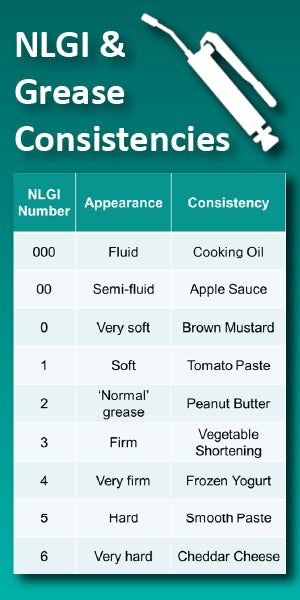
The NLGI grade is a measure of the relative hardness of a lubricant. It is the plastic resistance to deformation when a force is applied.
In the case of greases, it is hardness or softness, allowing the evaluation of flow and metering properties. It is evaluated according to the classification and parameters of the National Lubricating Grease Institute (USA).
NLGI grades 000 to 1
They are used in low viscosity applications in centralized lubrication systems requiring good pumpability, or gear units requiring a semi-fluid solution.
NLGI 2 Grades
This is the most common class of greases, including those for rolling bearings.
NLGI Grade 3 and 4
Thicker consistency used for valves and sealing joints.
NLGI Grade 5 and 6
These are solid lubricants offered in the form of briquettes.
Why use MOLYKOTE grease? ® 
- High temperature performance exceeding 180°C (356°F)
- Low temperature performance down to -40°C (-40°F) and in some cases less
- Resistance to chemicals such as solvents, fuels, acids and many others
- Good protection against corrosion thanks to resistance to moisture, oxidation and water washout
- Solid lubricants that increase the protection of abrasive surfaces
- Specialized bases containing silicone, fluorosilicone and PFPE (perfluoropolyether) oils.
Provide heavy-duty lubrication with industrial greases.
No matter your industry or needs, MOLYKOTE® brand industrial lubricants can withstand tough conditions. With a full range of high-performance greases – for solids and semi-solids with lubricant, thickener and additives – we have what you need:
Key applications for these greases include gears, all types of bearings, conveyor systems, guides, drives, pumps, valves, sockets and shafts. Meet your challenges with effective problem solvers for heavy-duty industrial lubrication.
Recommended MOLYKOTE® lubricants
These high performance lubricants provide exceptional friction control, wear resistance and load carrying properties at high and low temperatures. The following grease solutions are NLGI grade 2 and contain a thickener based on aluminum, polyurea, PTFE or lithium.| MOLYKOTE® Grease |
Base Oil Chemistry
|
Use or benefit
|
Temperature range
|
|---|---|---|---|
| MOLYKOTE BR-2 Plus® |
Mineral oil
|
Multitasking
|
From -20°F to 265°F
|
| MOLYKOTE G-4500FM® |
PAO (polyalphaolefin)
|
NSF H-1 Food Grade
|
From -40°F to 302°F
|
| MOLYKOTE G-4700® |
PAO (polyalphaolefin)
|
Molybdenum (MOS2) Synthetic Grease |
-40°F to 350°F
|
| MOLYKOTE G-1502FM® |
PAO (polyalphaolefin)
|
NSF H-1 Food Grade
|
From -40°F to 300°F
|
| MOLYKOTE BG-20® |
POE (polyol ester)
|
High-speed bearings
|
From -50°F to 360°F
|
| MOLYKOTE 33 Medium® |
Silicone oil
|
Extremely low temperature
|
From -99°F to 400°F
|
| MOLYKOTE 44 Medium® |
Silicone oil
|
Extremely high temperature
|
From -40°F to 400°F
|
| MOLYKOTE 3451® |
Fluorosilicone oil
|
Chemical resistance
|
-40°F to 450°F
|